Meaning of Wakf in Muslim Law
Wakf literally means tying up or detention. The one who makes Waqf is called Wakif. Deed is Wakf-nama.
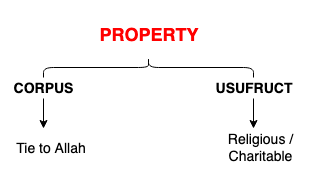
According to the accepted view, Wakf is the detention of the property in the ownership of God.
Quran is silent regarding Wakf, but Quran does say something about charity. In simple words, when a person ties up his property to God and keeps the usufruct for the benefit of the public. It may be religious or charitable.
Essentials of Wakf
1. There must be a permanent dedication of a property (movable or immovable).
2. By a person professing Islam.
3. For any purpose recognised by Islam.
Other Elements
1. There must be a clear intention on the part of the Wakif to create the Wakf. (Wakif is a creator of Wakf.)
2. Wakif must declare his intention either orally or in writing.
3. The Wakf must be perpetual, which means there should not be a fixed period.
4. The Wakif must be the owner of the property
5. The object of Wakf should not be in conflict with Islamic principles.
6. The Wakif must be of Muslim, major, and of sound mind. Wakf by minor is void ab initio. The guardian cannot create a Wakf on behalf of a minor.
7. Wakf should be by a person who is professing Islam.
Exceptionally, Wakf by a non-Muslim is recognised under certain conditions. It means a Wakf may be created by a person belonging to any religion, but in such a case, the object of Wakf must not be opposed to the creed (faith) of the Wakif.
It means a Muslim cannot create a Wakf for the construction of a Hindu temple, nor can a Hindu create a Wakf for the construction of a mosque.
But where the objects are secular in nature such as college, hospital, etc. then whether the Wakif is a Hindu or Muslim or Christian, the Wakf would be valid.
8. Wakf must not be contingent or conditional.
Legal effects of Wakf
1. Non-transferable
2. Irrevocable
3. Perpetual
Modes of Creation of Wakf
1. Inter vivos: transfer or gift made during one’s lifetime
2. By will (only one third)
3. By immemorial use
4. On death bed – Wakif can create only one third.
Note: Generally, a Wakf is irrevocable, but if the Wakf is created by will, then it may be revoked before the death of the testator.
Types of Wakf
1. Public Wakf → Waqf-ull-Allah (where the beneficiaries are public at large)
2. Private Wakf → Waqf-ull-Aulad (where the beneficiaries are the family member, relative, friends of Wakf)
What is Mutawalli
Mutawalli is the caretaker or manager of Waqf property. Wakif himself can also be Mutawalli.
Who may appoint Mutawalli?
1. Wakif himself
2. Executor
3. The Mutawalli appoints subsequent Mutawalli.
4. Court
5. Waqf Board
Who may be Mutawalli?
A trustworthy person and the person must be Muslim, major, male, and of sound mind.
A female or a non-Muslim may also be Mutawalli in a Wakf where the religious duties are not involved.
In simple words, a non-Muslim or female may be appointed the Mutawalli for a charitable or secular Wakf.
Minor as a Mutawalli
As a general rule, a minor cannot be appointed as a Mutawalli.
Syed Hasan vs. Mir Hasan: Court held that the minor Mutawalli is void. But where the office of Mutawalli is hereditary, and the person entitled to succeed the office is minor, then minor maybe a Mutawalli but court will appoint another person for taking care of the property till the age of 18 years.
Removal of Mutawalli
Once Mutawalli lawfully appointed cannot be removed except by the court.
Doctrine of Cypres
When the fulfilment of the object of Wakf becomes impossible, then Mutawalli may act for fulfilling any object which is similar to the object mentioned in Wakf.
Garib Das vs. M.A Hamid, 1970: Supreme Court held that a Wakf is completed by only a declaration by the Wakif. It may be oral or in writing. No formalities are needed for the creation of Wakf.
- Article 334A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024
- Article 332A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024
- Article 330A of the Constitution of India - 14th April 2024








