
In this Contract Act law note, you will learn about the five types of contracts with their definitions and easy examples. Later, you will also see the significant differences between void, voidable, and valid contracts.
What Is a Contract?
Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 defines a contract as “an agreement enforceable by law is a contract.” Initially, a contract is an agreement, an agreement is a promise, and a promise is an accepted proposal, which at a later stage becomes a contract if enforced by law.
Must Read: 9 Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
Kinds of Contract
Contracts are of five types. They are as follows:
Let us learn more about these five types of contacts with easy examples.
What Is a Void Contract?
Section 2(g) of the Indian Contract Act defines a void agreement as “an agreement not enforceable by law is said to be void.”
For example, an agreement with a minor is considered void ab inito (void from the beginning) because it cannot be enforced by the law.
What Is a Voidable Contract?
Section 2(i) of the Indian Contract Act says that “an agreement which is enforceable by law at the option of one or more of the parties thereto, but not at the option of other or others, is a voidable contract.”
If the decision or consent of a party to enter a contract is influenced by coercion, undue influence, misrepresentation, mistake, or fraud is considered a voidable contract. The party whose consent was influenced is given an option to continue with the said contract or strike it down. In such a case, the aggrieved party can claim damages, and if he gets any benefit out of the same, then he must restore it as well.
For example, Mr A asks for a bottle of sanitiser from ABC company, but the shopkeeper mistakenly gives him sanitiser from XYZ company. Now, Mr A has the option of returning it and getting the sanitiser of his choice of company or continuing with what the shopkeeper gave him.
What Is a Valid Contract?
Any agreement that fulfils all the essentials and is enforceable by law is to be considered a valid contract. As laid down by section 10 of the Indian Contract Act, which says, “all agreements are contracts if they are made by the free consent of parties competent to contract, for a lawful consideration and with a lawful object, and are not hereby expressly declared to be void.”
For example, Mr A offers Mr B to sell him his bike for Rs. 5,00,000 on Sunday. Mr B accepts the offer with the specified amount and the day. Here, Mr B willingly accepts the offer with all the valid terms laid down by the offeror; hence, it is a valid contract.
What Is an Illegal Agreement?
When the object of the agreement is illegal itself, then it cannot be enforced by law. Illegal contracts are void ab initio (void from the beginning). The court does not provide any remedy to any of the parties involved in such a contract. Even the transactions ancillary to the main object of the contract become illegal.
For example, to kill Mr A, Mr B borrows money from Mr D and gives it to Mr C. Since the objective of the agreement is illegal, it cannot be enforced by law. And the money transaction between Mr B and Mr D becomes void as Mr D knew Mr B’s purpose.
What Is an Unenforceable Contract?
These contracts are valid in the eyes of the law but cannot be enforced due to some technical or other issues. Such issues make such contracts incapable of being enforced by law.
For example, non-fulfilment of required documents in a prescribed manner (absence of stamp duty, signature, etc.)
Once the requirements are fulfiled or the errors are rectified, such a contract will be able to be enforced by the law again.
Read Next: What Are E-Contracts as Per the Indian IT Act?
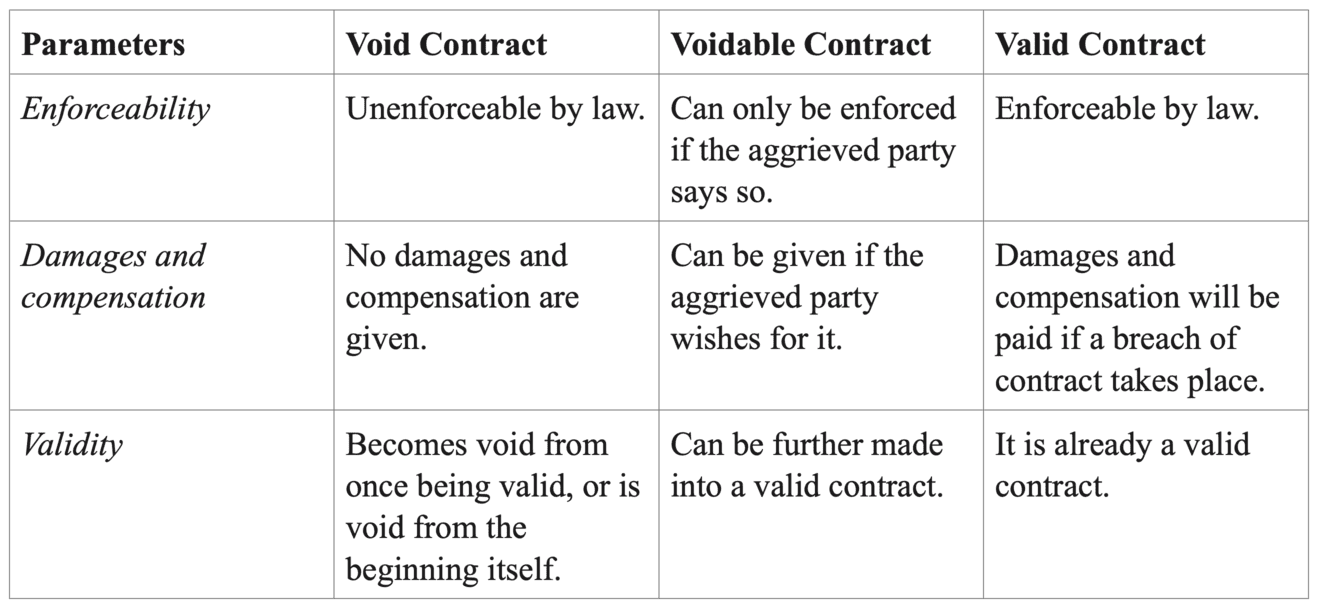
Differences Between Void, Voidable, and Valid Contracts
Some of the differences between void, voidable and valid contracts are:
Enforceability
- Void Contract: Unenforceable by law.
- Voidable Contract: It can only be enforced if the aggrieved party says so.
- Valid Contract: Enforceable by law.
Damages and compensation
- Void Contract: No damages and compensation are given.
- Voidable Contract: It can be given if the aggrieved party wishes for it.
- Valid Contract: Damages and compensation will be paid if a breach of contract takes place.
Validity
- Void Contract: Becomes void from once being valid or is void from the beginning itself.
- Voidable Contract: It can be further made into a valid contract.
- Valid Contract: It is already a valid contract.
Here’s the same information in tabular form:
Read Next:
1. Capacity to Contract Under the Indian Contract Act
2. What Is a Contract of Guarantee in Contract Act
3. Important Doctrines Under the Indian Contract Act
4. What Are Government Contracts in India?
- What Does “Justice Delayed Is Justice Denied” Mean? - 28th April 2023
- What Is Volenti Non-Fit Injuria Under the Law of Torts? - 25th April 2023
- What Are the Differences Between Possession and Custody? - 24th April 2023







